binding模块
在iBatis(Mybatis的前身)中,在查询一个Blog对象的时候会调用SqlSession.queryForObject("selectBlog",blogId)方法。其中,SqlSession.queryForObject()方法会执行指定的SQL语句进行查询并返回一个结果对象,第一个参数“selectBlog”指明了具体执行的SQL语句的id,该SQL语句定义在相应的映射配置文件中。如果我们错将“selectBlog”写成了“selectBlog1”,在初始化过程中,Mybatis是无法提示该错误的,而在实际调用queryForObject("selectBlog1",blogId)方法时才会抛出异常,开发人员才能知道该错误。
Mybatis提供了binding模块用于解决上述问题,我们可以定义一个接口(Mapper接口),该示例中为TbBlogMapper接口,具体代码如下所指示。注意,这里的TbBlogMapper接口并不需要去继承任何其它接口,而且开发人员不需要提供该接口的实现。
/**
* @author : <a href="mailto:gnehcgnaw@gmail.com">gnehcgnaw</a>
* @since : 2019/12/3 15:56
*/
public interface TbBlogMapper {
List<Map> selectBlogDetails1(@Param("id") int id);
List<TbBlog> selectBlogDetails2(@Param("id") int id);
List<TbBlog> selectBlogDetails3(@Param("id") int id);
List<Map> selectBlogList();
}
该Mapper接口中定义了SQL语句对应的方法,这些方法在Mybatis初始化过程中会与映射配置文件中定义的SQL语句相关联。如果存在无法关联的SQL语句,在Mybatis的初始化过程中节点就会抛出异常。我们可以通过调用Mapper接口中的方法执行相应的SQL语句,这样编译器就可以帮我们提早发现上述问题。查询Blog对象就变成了如下代码:
BlogMapper blogMapper = sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
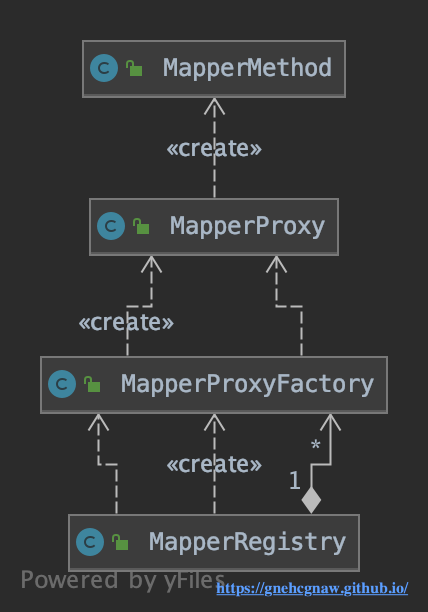
System.out.println(blogMapper.selectBlog(1));在开始分析binding模块的实现之前,先了解一下该模块中核心组件之间的关系,如图所示(Mybatis3.4版本):
在Mybatis3.5的时候,引入了MapperMethodInvoker,引入原因在后续源码分析中会介绍,所以核心组件之间的关系就发生了变化,如图所示:
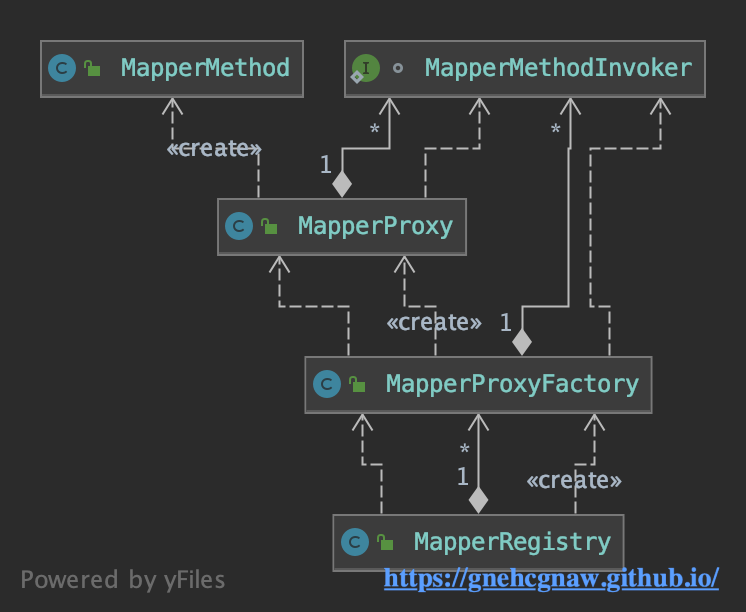
1. MapperRegistry
MapperRegistry是Mapper接口及其对应的代理工厂的注册中心,MapperRegistry中字段的含义如下所示:
/**
* Configuration对象,Mybatis全局唯一的配置对象,其中包含了所有配置信息
*/
private final Configuration config;
/**
* 记录了Mapper接口与定义{@link MapperProxyFactory}之间的关系
*/
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();1.1. addMapper()
在Mybatis初始化过程中会读取映射配置文件以及Mapper接口中的注解信息(XMLConfigBuilder.mapperElement(),并调用MapperRegistry.addMapper()方法填充MapperRegistry.knownMappers集合),knownMappers集合的key是Mapper接口对应的Class对象,value为MapperProxyFactory对象,MapperProxyFactory可以为Mapper接口创建代理对象,MapperProxyFactory的实现马上就会分析到。MapperRegistry.addMapper()方法实现如下:
/**
* 添加Mapper
* {@link org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder#mapperElement(XNode)} 中调用了addMapper(Class)
* @param type
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
//判断是不是接口类型
if (type.isInterface()) {
//是接口类型
//判断Configuration.knownMappers中是否已经有了,即检测是否已经加载过该接口
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
//将Mapper接口对应的Class对象和MapperProxyFactory对象添加到knownMappers集合
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
在Mybatis3.2.2之后的版本,addMapper()多了两个方法重载,具体如下所示:
/**
* @since 3.2.2
*/
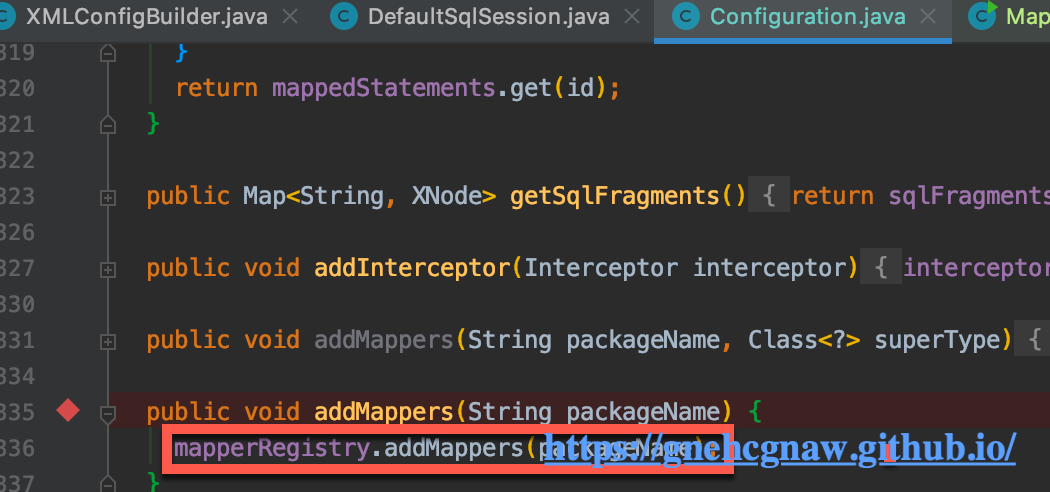
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) {
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
/**
* @since 3.2.2
*/
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}这样就可以加载那些,没有mapper.xml配置文件对应的Mapper接口,而这些接口凭借注解,也可以完成相应的操作,示例如下所示:
定义
CommentMapper接口package red.reksai.bingding.mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import java.util.Map; /** * @author : <a href="mailto:gnehcgnaw@gmail.com">gnehcgnaw</a> * @since : 2019/12/8 16:25 */ @Mapper public interface CommentMapper { @Select("select * from tb_comment where comment_id = #{id}") public Map selectTbComment(@Param("id")int id); }修改
mybatis-config.xml配置<!--在<mappers>内,<mapper>下添加如下配置--> <package name="red.reksai.bingding.mapper"/>调用
addMappers()方法调用链:
XMLConfigBuider.mapperElement()–>MapperRegistry.addMappers()。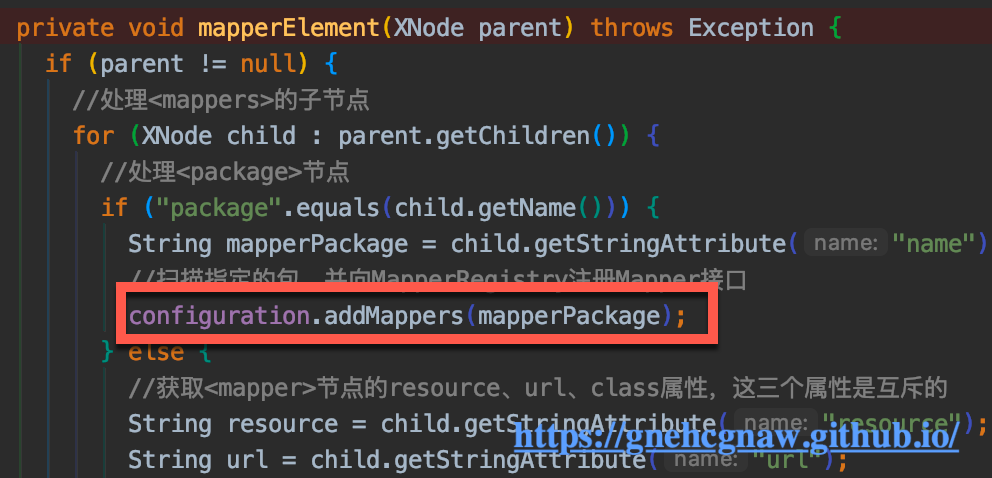
1.2. getMapper()
在需要执行某SQL语句时,会先调用MapperRegistry.getMapper()方法获取实现了Mapper接口的代理对象,例如:sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(CommentMapper.class)方法得到的实际上是Mybatis通过jdk动态代理为CommentMapper接口生成的代理对象,如下图所示:
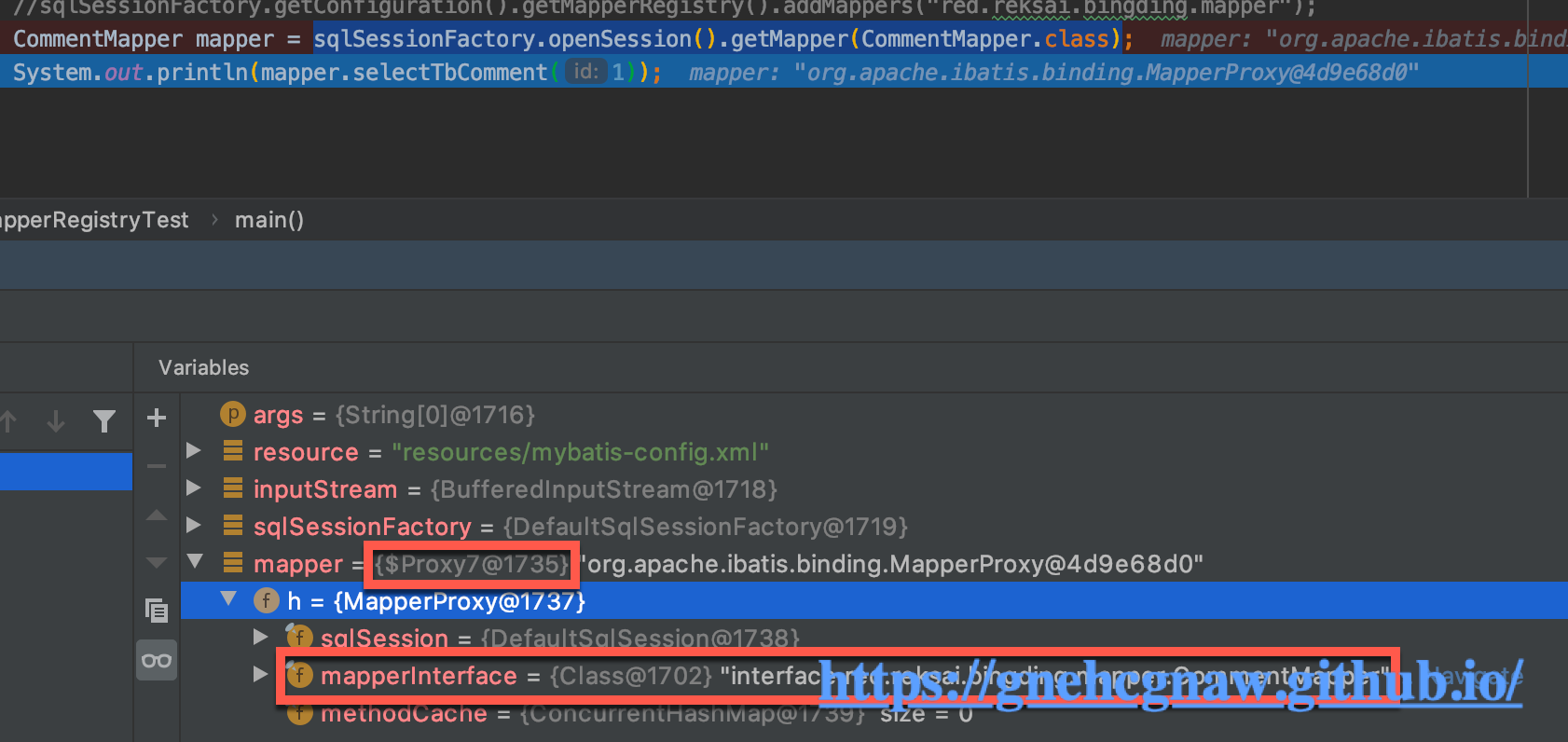
MapperRegistry.getMapper()方法的代码如下所示:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//查找指定的type对应的MapperProxyFactory对象
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
//如果mapperProxyFactory为空,则抛出异常
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//如果mapperProxyFactory不为空,则生成Mapper接口的代理对象并返回
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}2. MapperProxyFactory
MapperProxyFactory主要负责创建代理对象,其中核心字段的含义如下所示:
/**
* 需要代理的MapperInterface对象
*/
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/**
* 缓存
* key 是 mapperInterface接口中某方法对应的Method对象;
* value 是 对应的MappedMethodInvoker
*/
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();MapperProxyFactory.newInstance()方法实现了mapperInterface接口的代理对象的功能,具体代码如下所示:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//创建实现了MapperInterface接口的代理对象,从这里可以看出MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler接口
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//创建MapperProxy对象,每次调用都会创建新的MapperProxy对象
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}3. MapperProxy
MapperProxy在Mybatis3.4版本和mybatis3.5版本是有很大差别的,分别分析不同版本的代码,了解Mybatis官方为什么要这么做?
3.1. Mybatis3.4的MapperProxy
Mybatis3.4的MapperProxy只展示代码,分析在下面的Mybatis3.5的MapperProxy中进行。
MapperProxy中核心字段的含义如下:
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;MapperProxy.invoke()方法,如下所示:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}MapperProxy.cachedMapperMethod()方法,如下所示:
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}MapperProxy中的其他方法,如下所示:
@UsesJava7
private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class
.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return constructor
.newInstance(declaringClass,
MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC)
.unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
/**
* Backport of java.lang.reflect.Method#isDefault()
*/
private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) {
return (method.getModifiers()
& (Modifier.ABSTRACT | Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.STATIC)) == Modifier.PUBLIC
&& method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}3.2. Mybatis3.5的MapperProxy&MapperProxy.MapperMethodInvoker
MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler接口,那么该类的实现就是代理对象的核心逻辑,MapperProxy中核心字段的含义如下:
/**
* MethodHandles.Lookup 允许查找的模式
*/
private static final int ALLOWED_MODES = MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC;
/**
* MethodHandles.Lookup的Constructor对象,针对Java8
*/
private static final Constructor<Lookup> lookupConstructor;
/**
* 针对Java9
*/
private static final Method privateLookupInMethod;
/**
* 记录了关联的SqlSession对象
*/
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
/**
* mapperInterface接口对应的class对象
*/
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/**
* 缓存
* key 是 mapperInterface接口中某方法对应的Method对象;
* value 是 对应的MappedMethodInvoker
*/
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache;
MapperProxy在初始化的时候,首先要加载如下静态代码段,具体如下所示:
static {
Method privateLookupIn;
try {
// privateLookupIn 是java9中才有的(该方法可以模拟目标类上所有受支持的字节码行为,包括私有访问)
// 参见:https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/java/lang/invoke/MethodHandles.html
privateLookupIn = MethodHandles.class.getMethod("privateLookupIn", Class.class, MethodHandles.Lookup.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
privateLookupIn = null;
}
privateLookupInMethod = privateLookupIn;
Constructor<Lookup> lookup = null;
//判断privateLookupInMethod是不是为空,如果为空表明当前的jdk版本低于jdk9,大于等于jdk1.7,
//因为MethodHandles是jdk1.7才提供的功能
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
// JDK 1.8
try {
//获取MethodHandles.Lookup中参数列表为(Class<?> lookupClass, int allowedModes)的构造器
lookup = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
//将构造器设置为可访问的
lookup.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"There is neither 'privateLookupIn(Class, Lookup)' nor 'Lookup(Class, int)' method in java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles.",
e);
} catch (Exception e) {
lookup = null;
}
}
lookupConstructor = lookup;
}
刚开始看如上代码有点懵逼,因为我的java.lang.MethodHandles中并没有找到方法名称为privateLookupIn的方法,后来根据参看Java官方文档(Java9版本)发现这是Java9新增的一个方法,通过查看官方文档关于这个方法的描述,也就读懂了上面的代码。
对比Mybatis3.4是没有这段的,我发现引入了MethodHandle,引入的原因其实很简单:一是为了提高性能,二是为了安全,具体可以参看Java9版本关于MethodHandle的相关描述。
我这里简单带一下思路:其实都是为了实现动态代理,只不过加入MethodHandle之后,流程发生了一点消息的变化,我写了一个简单的Demo,如下所示:
@Test
public void test1() throws Throwable{
MethodHandles.Lookup lookup = MethodHandles.lookup();
MethodHandle replace = lookup.findVirtual(String.class, "replace", MethodType.methodType(String.class, char.class, char.class));
System.out.println((String) replace.invoke("zhangsan", Character.valueOf('g'), '_'));
}通过Demo发现要想执行invoke方法要分如下三步:
- 获取
Lookup对象,通过MethodHandles.lookup(),返回MethodHandles.Lookup对象; - 根据得到的
lookup对象去查找要执行的方法,并返回其封装的MethodHandle对象; - 根据得到的
methodHandle对象,调用invoke()方法去执行要代理对象要执行的方法。
不管是Mybatis3.4和3.5版本,MapperProxy.invoke()方法还是MapperProxy中的重中之重,Mybatis3.5的invoke()方法如下所示:
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
//如果当前方法是Object中的方法,直接invoke就可以了
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
//如果当前方法不属于Object对象的方法,
//那么:
// 1. 从缓存中查找
// 2. 调用invoke方法进行执行
// 参见: red.reksai.javabase.MethodHandlesTest
return cachedInvoker(proxy, method, args).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}发现其调用了cachedInvoke()方法,cachedInvoke()如下所示:
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//从缓存中查找method是否存在,如果不存在就创建一个并存入集合
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
//判断当前方法是不是default类型的方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
//是default类型的方法
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
//Java8
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
//Java9
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
//不是default类型的方法,就创建一个PlainMethodInvoker对象,并返回
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}以上代码还涉及到如下代码的调用,MapperProxy的其他方法,如下所示:
private MethodHandle getMethodHandleJava9(Method method)
throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return ((Lookup) privateLookupInMethod.invoke(null, declaringClass, MethodHandles.lookup())).findSpecial(
declaringClass, method.getName(), MethodType.methodType(method.getReturnType(), method.getParameterTypes()),
declaringClass);
}
private MethodHandle getMethodHandleJava8(Method method)
throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return lookupConstructor.newInstance(declaringClass, ALLOWED_MODES).unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass);
}
/**
* MapperMethod调用
*/
interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
}
/**
* 普通方法调用
*/
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
/**
* 默认方法调用
*/
private static class DefaultMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MethodHandle methodHandle;
public DefaultMethodInvoker(MethodHandle methodHandle) {
super();
this.methodHandle = methodHandle;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return methodHandle.bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
}通过以上代码的分析,结合如下示例,我用时序图的形式描述了其执行流程,如下图所示:
CommentMapper mapper = sqlSessionFactory.openSession().getMapper(CommentMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectTbComment(1));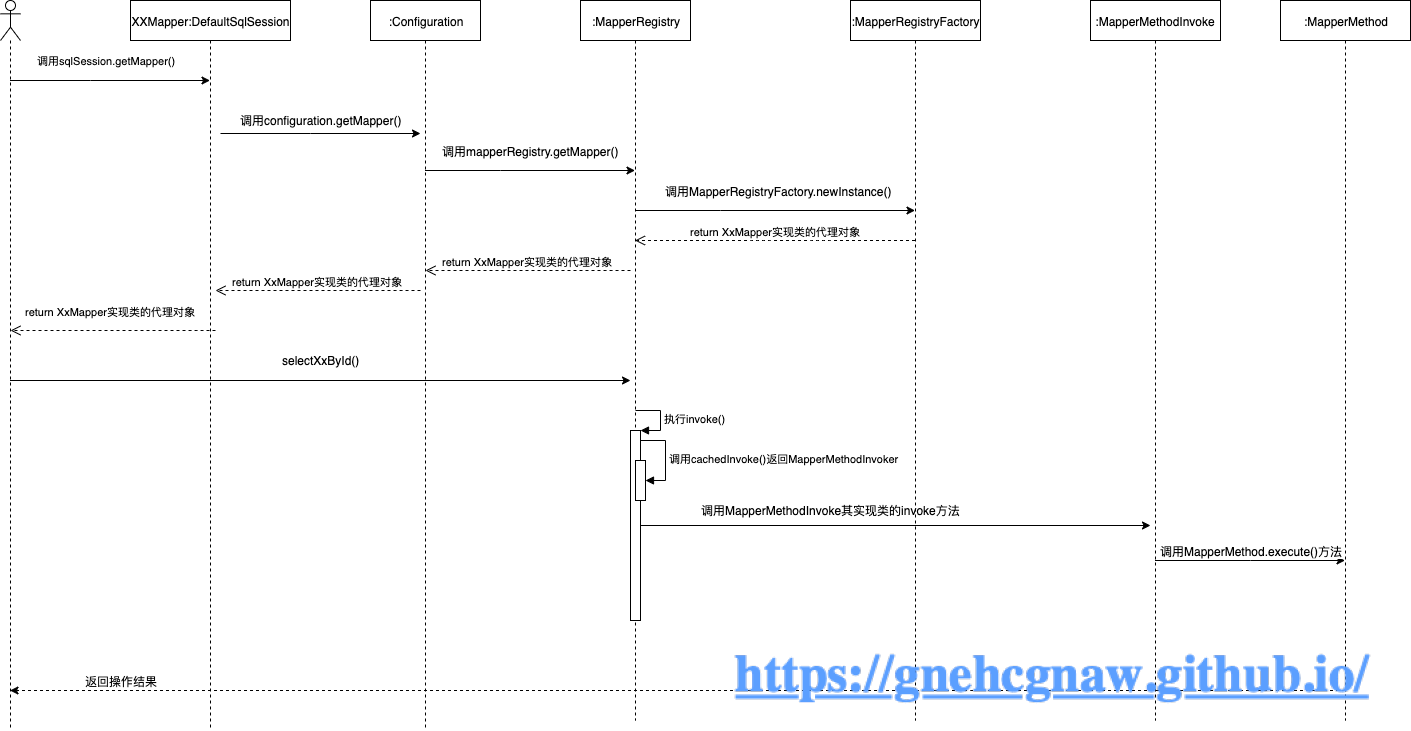
根据执行的时序图,我们接下来就应该去分析MapperMethod类了。
4. MapperMethod
MapperMethod中封装了Mapper接口中对应方法的信息,以及对应SQL语句的信息,MapperMethod可以看做是Mapper接口以及映射配置文件中定义的SQL语句的桥梁。MepperMethod中各个字段的信息如下:
/**
* 记录了SQL语句的名称和类型
*/
private final SqlCommand command;
/**
* Mapper接口中对应方法的相关新
*/
private final MethodSignature method;4.1. SqlCommand
SqlCommand是MapperMethod中定义的静态内部类,它使用了name字段记录SQL语句的名称,使用type字段(SqlCommandType类型)记录了SQL语句的类型。SqlCommandType是枚举类型,有效值UNKNOWN、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、SELECT、PLUSH。SqlCommand的构造方法会初始化name字段和type字段,代码如下:
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
//获取方法的名称
final String methodName = method.getName();
//获取声明类
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
//获取对应的MapperStatement对象
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
//判断MappedStatement对象是否为空
if (ms == null) {
//判断当前方法上是不是有@Flush注解
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}以上代码有个作用于Method的注解@Flush,这个注解的作用在后续进行讲解。
4.2. MethodSignature
MethodSignature也是MapperMethod中定义的内部类,其中封装了Mapper接口中定义的方法的相关信息,MethodSignature核心字段如下所示:
/**
* 返回值类型是否为Collection类型或者是数组类型
*/
private final boolean returnsMany;
/**
* 返回值类型是否是Map类型
*/
private final boolean returnsMap;
/**
* 返回值类型是否为Void类型
*/
private final boolean returnsVoid;
/**
* 返回值是否是Cursor类型
*/
private final boolean returnsCursor;
/**
* 返回值是否是Optional类型
*/
private final boolean returnsOptional;
/**
* 返回值类型
*/
private final Class<?> returnType;
/**
* 如果返回值类型是Map,则该字段记录了作为key的列名
*/
private final String mapKey;
/**
* 用来标记该方法参数列表中ResultHandler类型参数的位置
*/
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
/**
* 用来标记该方法参数列表中RowBounds类型参数位置
*/
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
/**
* 该方法对应的ParamNameResolver对象
*/
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;在MethodSignature的构造函数中会解析相应的Method对象,并初始化上述字段,具体代码如下所示:
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
//解析方法的返回值类型
Type resolvedReturnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, mapperInterface);
//初始话MethodSignature的字段
if (resolvedReturnType instanceof Class<?>) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) resolvedReturnType;
} else if (resolvedReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType) {
this.returnType = (Class<?>) ((ParameterizedType) resolvedReturnType).getRawType();
} else {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
}
//初始化returnsVoid、returnsMany、returnsCursor、returnsOptional字段
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray();
this.returnsCursor = Cursor.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsOptional = Optional.class.equals(this.returnType);
//若Method对应的方法的返回值是Map且指定了@MapKey注解,则使用getMapKey()方法处理
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = this.mapKey != null;
//初始话rowBoundsIndex
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
//初始化resultHandlerIndex
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
//创建ParamNameResolver对象
this.paramNameResolver = new ParamNameResolver(configuration, method);
}以上代码涉及到如下几个重要方法或对象:
4.2.1. getMapKey()
getMapKey()的代码如下所示:
private String getMapKey(Method method) {
String mapKey = null;
//首先判断返回值类型是不是Map
if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())) {
//是map
//看有没有MapKey注解
final MapKey mapKeyAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MapKey.class);
if (mapKeyAnnotation != null) {
//有MapKey注解则返回,对应的值
mapKey = mapKeyAnnotation.value();
}
}
return mapKey;
}@MapKey作用于Method,在后续讲解中会涉及到,这里只做结果演示:
@Select("select author_id , author_username from tb_author where author_username = #{name} order by author_id desc")
Map selectAuthorByName(@Param("name")String name);要查询的库,如下所示:

查询
authot_name=root,那么可以用map接收结果集,因为只有一条,结果是:{author_id=1, author_username=root}现在在
selectAuthorByName()方法上加上@MapKey("author_name")注解,同样还是查询authot_name=root,结果是:{root={author_id=1, author_username=root}},可以看出MapKey的作用就是指定map的key,把结果集作为value。查询
authot_name=lisi,那么正常情况下结果集应该是个List,如果用Map接收会报一个结果集不唯一的异常,但是加上@MapKey("author_name")注解之后就不一样了,结果是:{lisi={author_id=3, author_username=lisi}},我们发现返回值只有一条,说明结果集被覆盖了,因为是用key是lisi,根据Map的特性,key为lisi的数据只有一条。
这里只是把这种现象演示出来,后面会涉及到如果方法上有MapKey标记,Mybatis是如何处理的?
4.2.2.getUniqueParamIndex()
getUniqueParamIndex()方法的主要功能是查找指定类型的参数在参数列表中的位置,如下:
private Integer getUniqueParamIndex(Method method, Class<?> paramType) {
Integer index = null;
final Class<?>[] argTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
//遍历MethodSignature对应方法的参数列表
for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; i++) {
if (paramType.isAssignableFrom(argTypes[i])) {
if (index == null) {
//记录paramType类型参数在参数列表中的位置索引
index = i;
} else {
//RowBounds和ResultHandler类型的参数只能有一个,不能重复出现
throw new BindingException(method.getName() + " cannot have multiple " + paramType.getSimpleName() + " parameters");
}
}
}
return index;
}4.2.3.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam()
MethodSignature还提供了对应字段的getter/setter方法,其中convertArgsToSqlCommandParam()方法需要介绍一下:
/**
* 负责将agr[]数组(用户传入的实参列表)转化成SQL语句的参数列表,它是通过ParamNameResolver.getNamedParams()方法完成的。
* @param args
* @return
*/
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
4.3. execute()
分析完MapperMethod中定义的内部类之后,回到MapperMethod继续分析。MapperMethod的核心方式execute()方法,它会根据SQL语句的类型调用SqlSession对应的方法完成数据库操作。SqlSession是Mybatis的核心组件之一,其具体实现后面会详细介绍,这里暂时只需要知道它负责完成数据库操作即可。MapperMethod.execute()方法的具体实现如下:
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!