解析<resultMap>节点
1. 简介
select语句查询得到的结果集是一张二维表,水平方向上看是一个个字段,垂直方向上看是一条条数据。而Java是面向对象的程序设计语言,对象是根据类定义创建的,类之间的引用关系是可以认为是嵌套结构的。在JDBC编程中,为了将结果集中的数据映射成对象,我们需要自己写代码从结果集中获取数据,然后封装成对应的对象并设置对象之间的关系,而这些都是大量的重复性的代码。为了减少这些重复的代码,Mybatis使用<resultMap>节点定义了结果集与结果对象(JavaBean对象)之间的映射规则,<resultMap>节点可以满足绝大部分的映射需求,从未减少开发人员的重复性劳动,提高开发效率。
在开始介绍<resultMap>节点的解析过程之前,先来介绍该过程中使用的数据结构。每个ResultMapping对象记录了结果集中的一列与JavaBean中一个属性之间的映射关系。在后面的分析过程中我们可以看到,<resultMap>节点下除了<discriminator>子节点的其他子节点,都被解析成对应的ResultMapping对象。ResultMapping对象的核心字段如下所示:
/**
* Configuration对象
*/
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* 对应节点的property属性,表示的是与该列映射的属性
*/
private String property;
/**
* 对应节点的column属性,表示的是从数据库中得到的列名或列名的别名
*/
private String column;
/**
* 对应节点的javaType属性,表示的是一个JavaBean的完全限定名,或一个类型的别名
*/
private Class<?> javaType;
/**
* 对应节点的jdbcType属性,表示的是进行映射的列的JDBC类型
*/
private JdbcType jdbcType;
/**
* 对应节点的typeHandler属性, 表示的是类型处理器,它会覆盖默认的类型处理器,
*/
private TypeHandler<?> typeHandler;
/**
* 对应节点的resultMap属性,该属性通过id引用另一个<resultMap>节点定义,它负责将结果集中的一部分分列映射成其他关联的结果对象。
* 这样我们就可以通过join方式进行关联查询,然后直接映射多个对象,并同时设置这些对象之间的关系。
*/
private String nestedResultMapId;
/**
* 对应节点的select属性,该属性通过id引用了另一个<select>节点定义,它会把指定的列的值传入select属性指定的select语句中作为参数进行查询。
* 使用select属性可能会造成N+1问题。
*/
private String nestedQueryId;
/**
* 对应节点的notNullColumns属性拆分后的结果
*/
private Set<String> notNullColumns;
/**
* 对应节点的columnPrefix属性
*/
private String columnPrefix;
/**
* 处理后的标志,标志有两个:id和constructor
*/
private List<ResultFlag> flags;
/**
* 对应节点的column属性拆分后生成的结果,composites.size()>0会是column为null
*/
private List<ResultMapping> composites;
/**
* 对应节点的resultSet属性
*/
private String resultSet;
/**
* 对应节点的foreignColumn属性
*/
private String foreignColumn;
/**
* 对应节点的lazy属性,是否延迟加载
*/
private boolean lazy;
ResultMapping中定义了一个内部的Builer类,也应用了建造者模式,该builder类主要用于数据整理和数据校验,实现比较简单。
另一个主要的类是ResultMap,每个<resultMap>节点都会被解析成一个ResultMap对象,其中每个节点所定义的映射关系,则使用ResultMapping对象表示。
ResultMap中各个字段的含义如下:
/**
* Configuration对象
*/
private Configuration configuration;
/**
* <resultMap>的id属性
*/
private String id;
/**
* <resultMap>的type属性
*/
private Class<?> type;
/**
* 记录了除<discriminator>节点之外的其他映射关系(即:ResultMapping对象集合)
*/
private List<ResultMapping> resultMappings;
/**
* 记录了映射关系中带ID标志的映射关系,例如:<id>节点和<constructor>节点的<idArg>节点
*/
private List<ResultMapping> idResultMappings;
/**
* 记录映射关系中带constructor标志的映射关系,例如:<constructor>所有子元素
*/
private List<ResultMapping> constructorResultMappings;
/**
* 记录映射关系中不带constructor标志的映射关系
*/
private List<ResultMapping> propertyResultMappings;
/**
* 记录映射关系中所有的column属性
*/
private Set<String> mappedColumns;
/**
* 记录映射关系中所有的property属性
*/
private Set<String> mappedProperties;
/**
* 鉴别器,对应<discriminator>节点
*/
private Discriminator discriminator;
/**
* 是否有嵌套的结果集映射,如果某个映射关系中存在resultMap属性,且不存在resultSet属性,则为true
*/
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
/**
* 是否含有嵌套查询,如果某个属性映射存在select属性,则为true
*/
private boolean hasNestedQueries;
/**
* 是否开启自动映射
*/
private Boolean autoMapping;
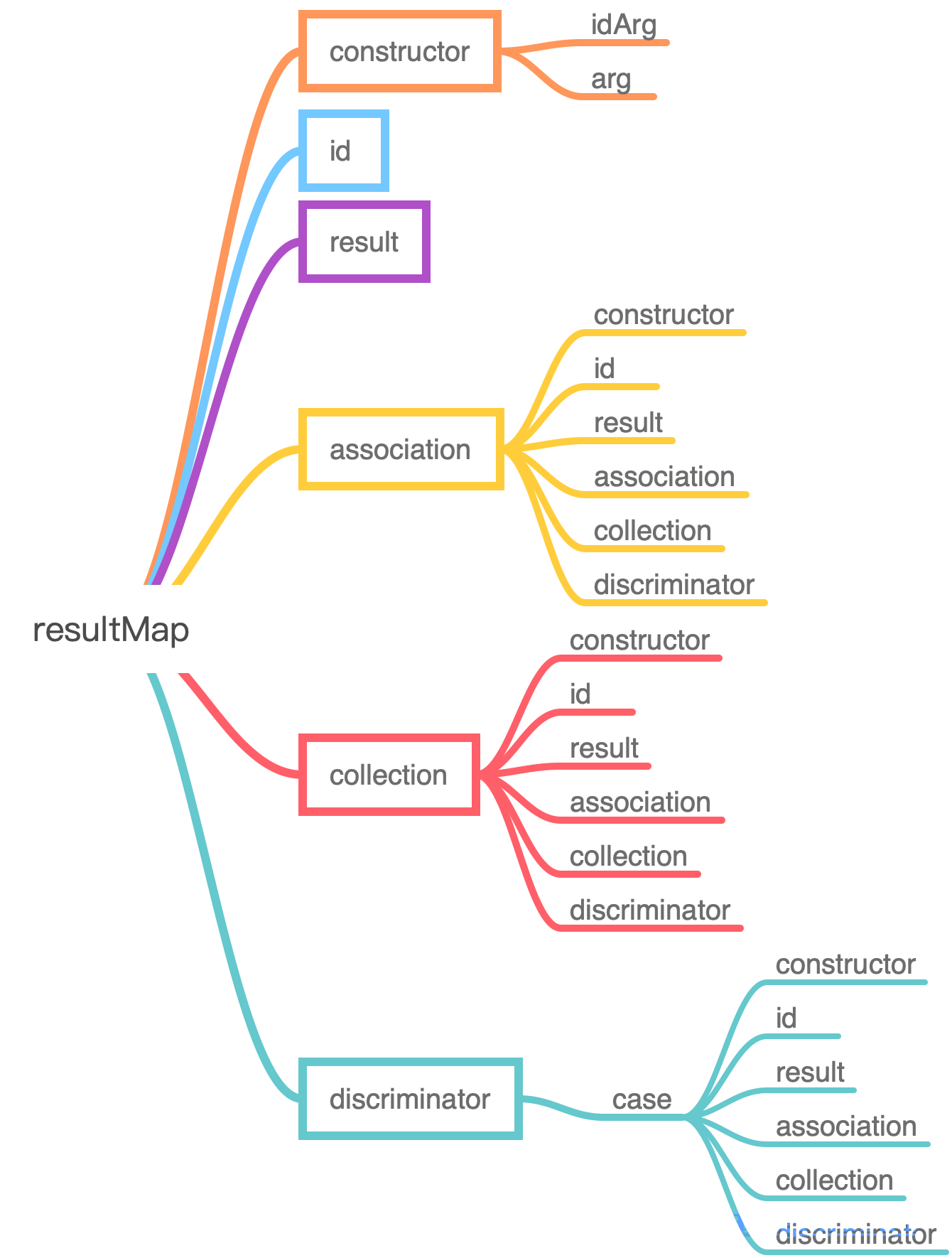
2. resultMap节点结构
2.1. resultMap下的子节点
2.2. resultMap节点属性表
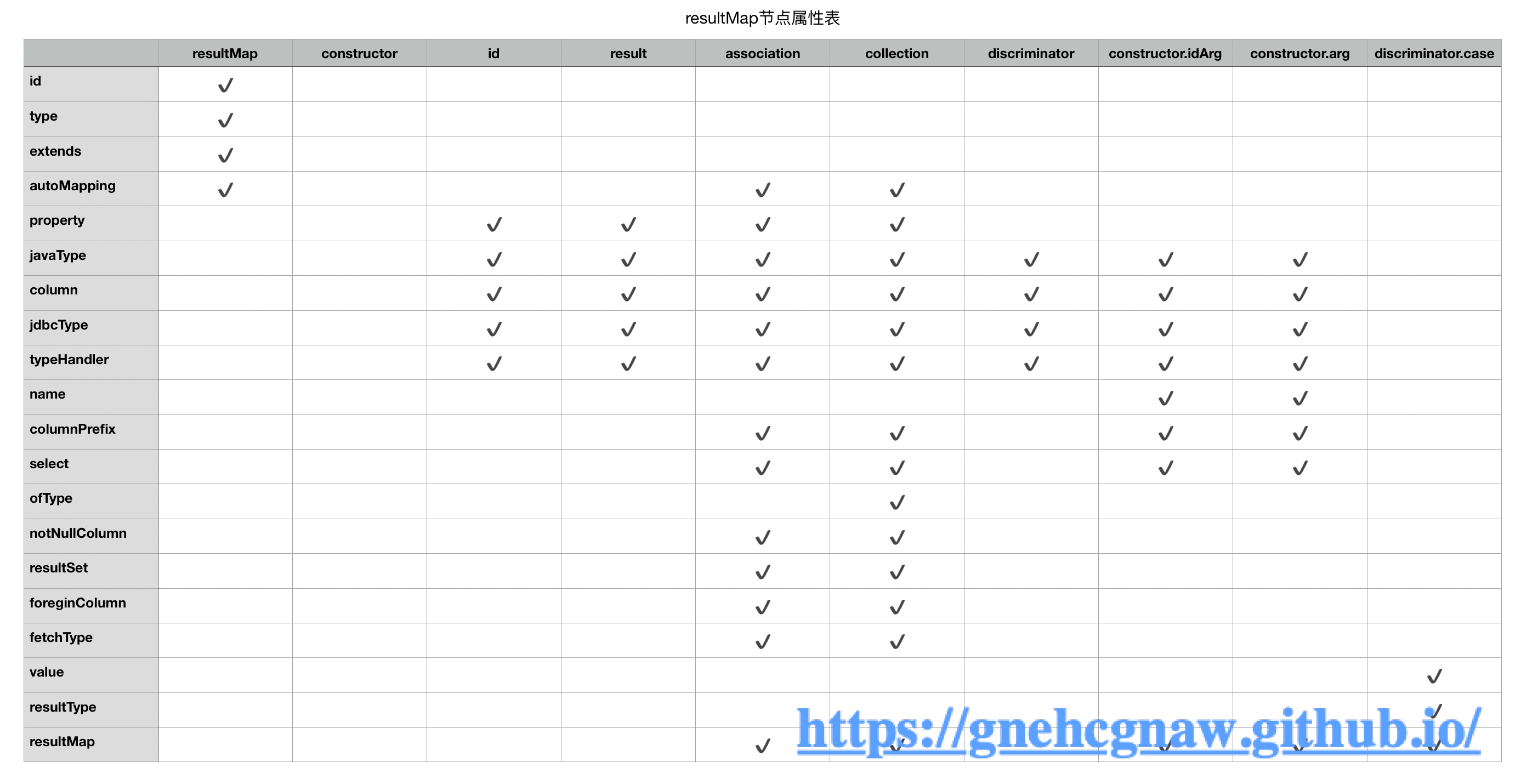
由图一可知:<resultMap>下的节点不只一层,而是可以无限嵌套;
由图二可知:association、collection、constructor下的isArg和arg、discriminiator下的case都可以定义属性resultMap;
结合ResulMap和ResultMapping类知道了在解析resultMap节点的时候势必要解析嵌套的resultMappings。
3. 解析resultMap节点涉及到的方法
解析resultMap节点涉及到的核心类和方法很多,具体如下所示:
XMLMapperBuilder
resultMapElement()
inheritEnclosingType()
processConstructorElement()
processDiscriminatorElement()
buildResultMappingFormContext()
processNestedResultMappings()
validateCollection()
MapperBuilderAssistant
- buildDiscriminator()
- buildResultMappings()
XNode
- getVauleBasedIdentifier()
ResultMapResolver
- resolve()
4. 结合示例分析Mybatis解析resultMap节点的过程
4.1. 示例一(resultMap节点下只有id和result)
<resultMap id="authorResultMap" type="TbAuthor">
<id property="authorId" column="author_id"/>
<result property="authorUsername" column="author_username"/>
<result property="authorPassword" column="author_password"/>
<result property="authorEmail" column="author_email"/>
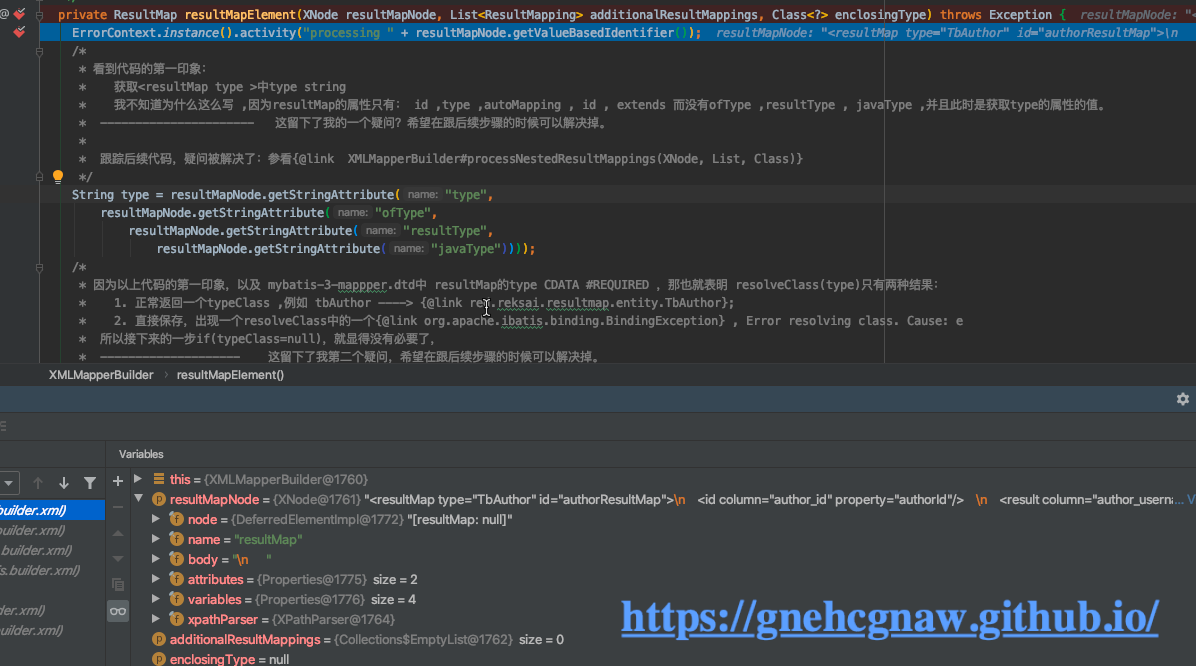
</resultMap>- 开始解析,解析
resultMap节点首先调用的方法就是resultMapElement(),如图所示:
- 根据以下
debug的显示,“以下代码主要是解析“(为什么用删除线往后读就知道了)。resultMap中type的属性值,并获取属性值对应的Class类型
//获取属性值
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
//获取resultMap映射的Class类型
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);
if (typeClass == null) {
typeClass = inheritEnclosingType(resultMapNode, enclosingType);
}结合上述列出的resultMap节点属性表可知:
type属性只存在于
<resultMap>中,而且必须定义为非空属性值;<resultMap>节点中不存在ofType、resultType、javaType属性;ofType属性只存在与
<collection>节点中;resultType属性可以存在于
<discriminator>节点的子节点<case>中;javaType属性可以存下于
<id>、<result>、<association>(以及<association>下的<idArg>和<arg>)、<collection>、<discriminator>节点中;
结合存在即合理的理论,可知:
- 上述的代码就不只是为了解析
<resultMap>节点中的属性了; - 也会解析上述所说的包含了
ofType、resultType、javaType的节点; - 也有可能解析不包含
ofType、resultType、javaType的节点,因为type==null的时候也可以调用inheritEnclosingType()方法返回一个typeClass对象。
那么就确定resultMapElement()方法,会被符合某些条件的节点调用,后续可知是processNestedResultMappings()方法中也调用了resultMapElement()。
- 初始化对象
Discriminator和resultMappings(List<ResultMapping>),并将存入的值add到resultMappings结合中(读到这里也就有了头绪,resultMapElement()方法的用途之一就是迭代将节点解析成ResultMapping对象并将其存入到resultMappings集合中),代码如下所示:
//初始化一个Discriminator,用于存放把<discriminator>节点解析的属性
Discriminator discriminator = null;
//初始化一个集合,该集合用于记录解析的结果
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);- 循环解析
<resultMap>节点下的所有子节点,代码如下所示:
//处理<resultMap>的子节点
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
//处理<constructor>节点
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
//处理<discriminator>节点
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
//处理<id>、<result>、<association>、<collection> 节点
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
//如果是<id>节点,则向flags集合中添加ResultFlag.ID
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
//创建ResultMapping对象,并添加到resultMappings集合
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}因为示例一中没有<constructor>和<discriminator>节点,所以程序会走到最后一个else中,而我们知道<resultMap>节点下还有<id>、<result>、<association>、<collection>节点,所以这个else中的代码会处理<id>、<result>、<association>、<collection>节点。
else中大的步骤可以分为三步:
- 创建一个
List<ResultFlag>,如果有节点名称为id,那么就添加一个ResultFlag.ID到集合中; - 调用
buildResultMappingFromContext()方法得到一个ResultMapping对象; - 将得到的
ResultMapping对象对象添加到resultMappings集合中。
其实最关键的代码一步就是调用buildResultMappingFromContext()方法返回一个ResultMapping对象。
- 通过buildResultMappingFromContext(),从上下文构建resultMapping,具体如下所示:
private ResultMapping buildResultMappingFromContext(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultFlag> flags) throws Exception {
String property;
if (flags.contains(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR)) {
// 如果是ID标识,则获取name属性的值 例如:constructor 下的idArg*,arg*,只有name,而没有property
property = context.getStringAttribute("name");
} else {
//如果是ID标识,则获取property属性的值 例如:<id property="authorId" column="author_id"/> property = "authorId"
property = context.getStringAttribute("property");
}
//获取column属性值
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
//获取javaType属性值
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
//获取jdbcType属性值
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
//获取select属性值
String nestedSelect = context.getStringAttribute("select");
//获取resultMap属性值,并处理其中嵌套的resultMapping
String nestedResultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap",
processNestedResultMappings(context, Collections.emptyList(), resultType));
//获取notNullColumn属性值
String notNullColumn = context.getStringAttribute("notNullColumn");
//获取columnPrefix属性值
String columnPrefix = context.getStringAttribute("columnPrefix");
//获取typeHandler属性值
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
//获取resultSet的属性值
String resultSet = context.getStringAttribute("resultSet");
//获取foreignColumn属性值
String foreignColumn = context.getStringAttribute("foreignColumn");
//设置lazy的值,会考虑全局的懒加载设置,如果局部属性没有设置fetchType的值,那么使用全部的设置
boolean lazy = "lazy".equals(context.getStringAttribute("fetchType", configuration.isLazyLoadingEnabled() ? "lazy" : "eager"));
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
//获取当前标签使用的typeHandler的实现类
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(typeHandler);
//获取jdbcType对应的类
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
//利用MapperBuilderAssistant构建ResultMappings
return builderAssistant.buildResultMapping(resultType, property, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, nestedSelect, nestedResultMap, notNullColumn, columnPrefix, typeHandlerClass, flags, resultSet, foreignColumn, lazy);
}其实这个方法很简单,就是获取构建ResultMapping对象的属性值,然后通过调用buildResultMapping()构建ResultMapping对象。只不过其中涉及调用processNestedResultMappings()处理嵌套ResultMapping,然后返回其属于的ResultMap的名称。
因为示例中没有resultMap属性,跟没有嵌套的resultMappings,示例一这种情况,nestedResultMap永远为空。
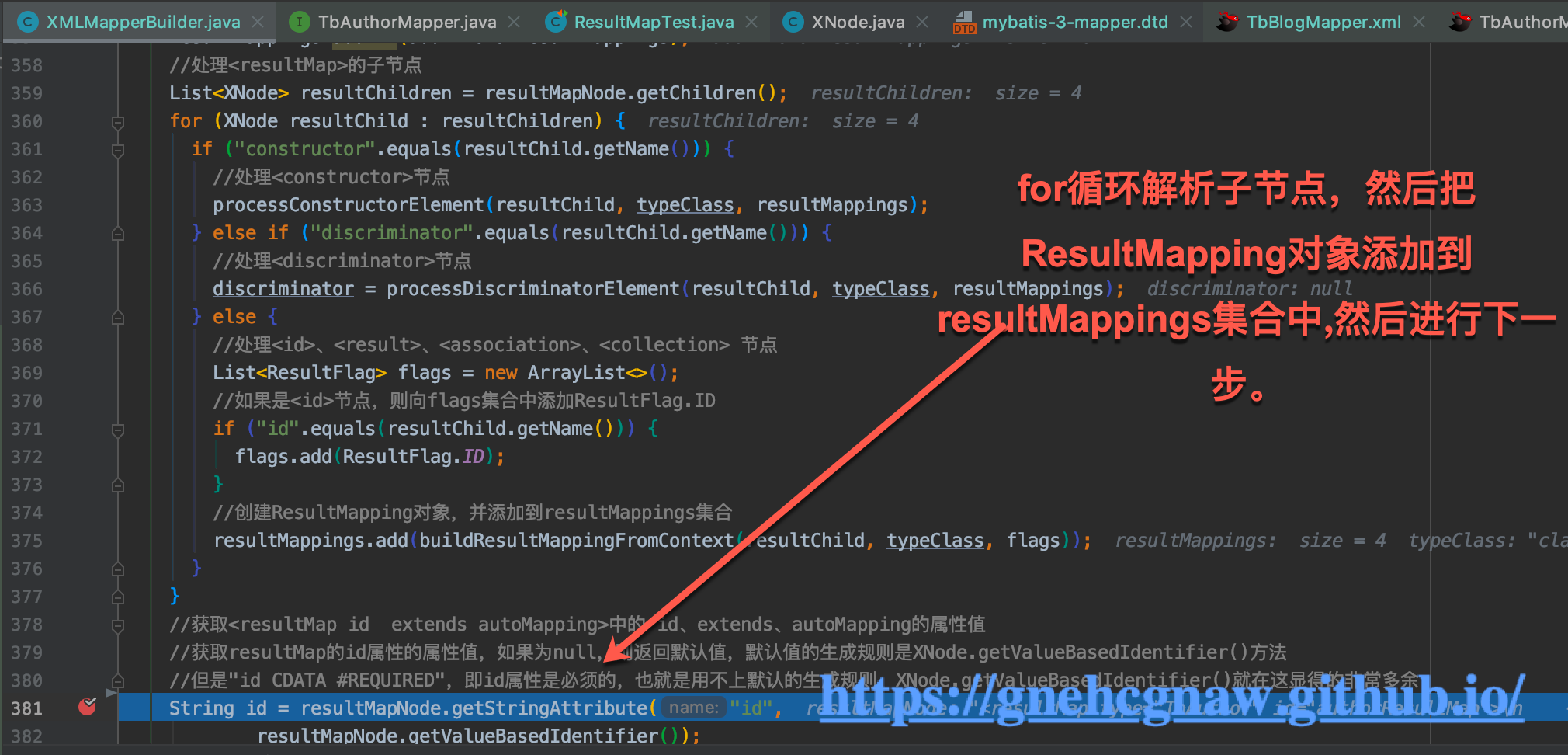
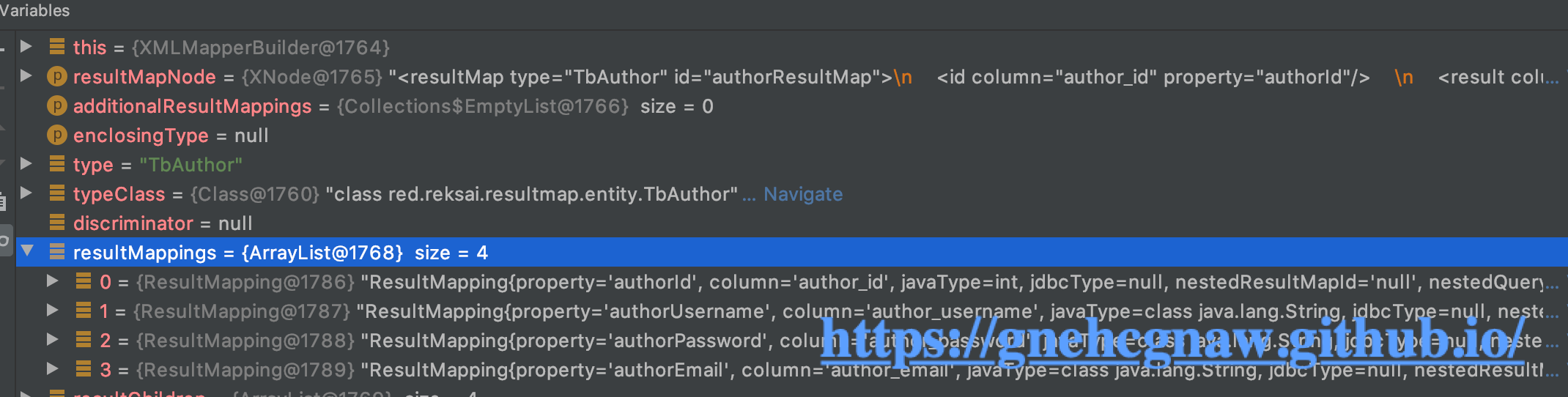
- 当示例一中
<resultMap>下所有的子节点通过for循环遍历解析完之后,返回到resultMapElement()方法的以下位置:
- 获取当
resultMap的id(如果没有通过XNoder.getValueBasedIdentifier()获取一个固定格式的id);获取extends的属性的值;获取autoMapping的属性的值,然后调用ResultMapResolver的resolve()方法完成ResultMap对象的创建和添加,添加到Configuration.resultMaps中,代码如下所示:
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//获取<resultMap>节点的extends属性的值,该属性指定了<resultMap>节点的继承关系
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
//获取<resultMap>节点的autoMapping属性的值
//如果该属性设置为true,则启动自动映射功能,即自动查找与列名相同的属性名,并调用setter方法。
//如果该属性设置为false,则需要在<resultMapping>节点内注明映射关系才能调用对应的setter方法。
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
//创建一个ResultMapResolver,并为当前的ResultMapResolver设置属性初始值,这些初始值会在ResultMapResolver的resolve()方法中派上用场
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
//创建ResultMap对象,并将其添加到Configuration.resultMap集合中,
return resultMapResolver.resolve();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
为什么解析了一个<resultMap>节点会向Configuration.resultMaps中添加两条记录?
这是因为resultMaps集合的类型是StrictMap,这个对象的put()方法如下所示:
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public V put(String key, V value) {
//如果检测到重复的key直接抛出异常
if (containsKey(key)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key
+ (conflictMessageProducer == null ? "" : conflictMessageProducer.apply(super.get(key), value)));
}
//如果没有重复的key则添加key以及value
//同时根据key产生shortKey
if (key.contains(".")) {
//按照“.”将key切分成数组,然后将数组的最后一项作为shortKey
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
//如果不包含指定shortKey,则添加该键值对
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value);
} else {
//如果该shortKey已经存在,则将value修改成Ambiguity对象
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey));
}
}
//如果没有重复的key则添加key以及value(这是全面)
return super.put(key, value);
}
4.2. 示例二(在示例一的基础上加上collection和association)
<resultMap id="selectBlogDetailsResultMap2" type="red.reksai.resultmap.entity.TbBlog">
<id property="blogId" column="blog_id" />
<result property="blogTitle" column="blog_title"/>
<!--关联的嵌套结果映射resultMap="red.reksai.resultmap.mapper.TbAuthorMapper.authorResultMap"-->
<association property="tbAuthor" resultMap="red.reksai.resultmap.mapper.TbAuthorMapper.authorResultMap" />
<collection property="tbPosts" ofType="red.reksai.resultmap.entity.TbPost" resultMap="red.reksai.resultmap.mapper.TbPostMapper.postResultMap" column="post_blog_id" >
<collection property="tbComments" ofType="red.reksai.resultmap.entity.TbComment"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>示例二和示例一唯一的不同就是有resultMap了,而且有嵌套的resultMappings了,代码体现就是进入到processNestedResultMappings()方法中的if中,具体如下所示:
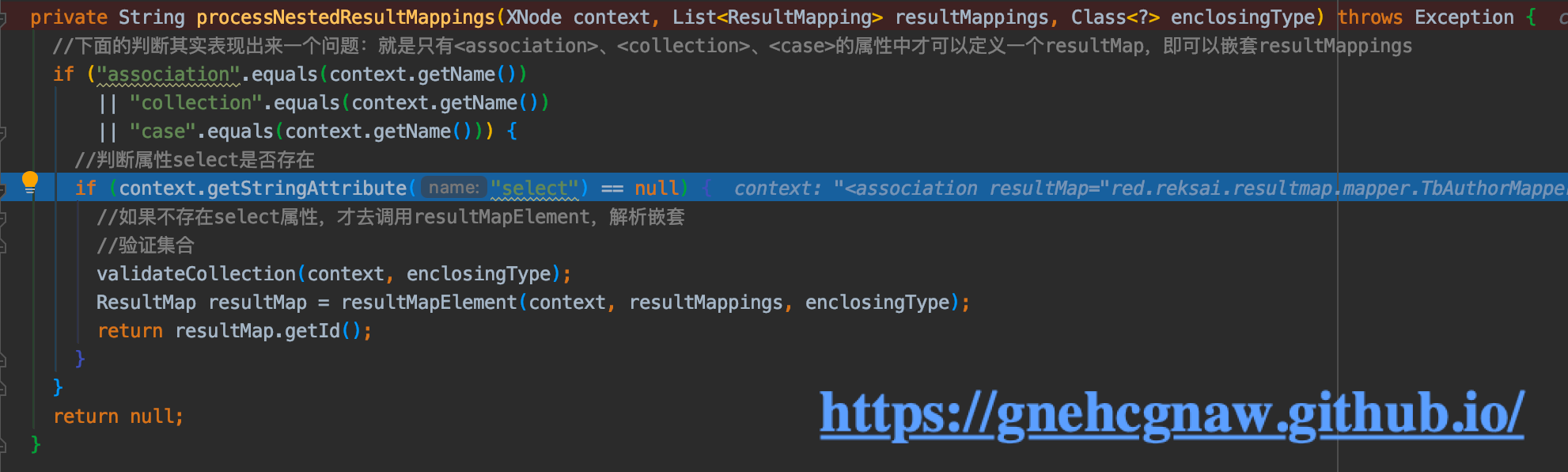
根据if判断内的条件,可知这里是处理
4.3. 示例三(在示例二的基础上加上constructor)
<resultMap id="selectBlogDetailsResultMap2" type="red.reksai.resultmap.entity.TbBlog">
<constructor>
<idArg column="blog_id" javaType="int"/>
</constructor>
<id property="blogId" column="blog_id" />
<result property="blogTitle" column="blog_title"/>
<!--关联的嵌套结果映射resultMap="red.reksai.resultmap.mapper.TbAuthorMapper.authorResultMap"-->
<association property="tbAuthor" resultMap="red.reksai.resultmap.mapper.TbAuthorMapper.authorResultMap" />
<collection property="tbPosts" ofType="red.reksai.resultmap.entity.TbPost" resultMap="red.reksai.resultmap.mapper.TbPostMapper.postResultMap" column="post_blog_id" >
<collection property="tbComments" ofType="red.reksai.resultmap.entity.TbComment"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>如果有<constructor>子节点,会进入processConstructorElement()方法,具体如下所示:

private void processConstructorElement(XNode resultChild, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
//获取<constructor>下的子节点
List<XNode> argChildren = resultChild.getChildren();
for (XNode argChild : argChildren) {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<>();
//添加CONSTRUCTOR标志
flags.add(ResultFlag.CONSTRUCTOR);
//如果包含idArg,添加ID标志
if ("idArg".equals(argChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
//创建ResultMapping对象,并添加到resultMappings集合中
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(argChild, resultType, flags));
}
}4.4. 示例四(在示例三的基础上加上了discriminator)
<discriminator javaType="int" column="draft">
<case value="1" resultType="DraftPost"/>
</discriminator>private Discriminator processDiscriminatorElement(XNode context, Class<?> resultType, List<ResultMapping> resultMappings) throws Exception {
String column = context.getStringAttribute("column");
String javaType = context.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcType = context.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String typeHandler = context.getStringAttribute("typeHandler");
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaType);
Class<? extends TypeHandler<?>> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(typeHandler);
JdbcType jdbcTypeEnum = resolveJdbcType(jdbcType);
Map<String, String> discriminatorMap = new HashMap<>();
for (XNode caseChild : context.getChildren()) {
String value = caseChild.getStringAttribute("value");
//case节点内是可以定义resultMap的,所以还要去迭代解析直到所有的嵌套的resultMap解析完成为止
String resultMap = caseChild.getStringAttribute("resultMap", processNestedResultMappings(caseChild, resultMappings, resultType));
discriminatorMap.put(value, resultMap);
}
return builderAssistant.buildDiscriminator(resultType, column, javaTypeClass, jdbcTypeEnum, typeHandlerClass, discriminatorMap);
}本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!