反射工具箱
1. 简介
Mybatis在进行参数处理、结果集映射等操作时,会涉及大量的反射操作。Java中的反射虽然功能强大,但是代码编写起来比较复杂容易出错,为了简化反射操作的相关代码,Mybatis提供了专门的反射模块,该模块位于org.apache.ibatis.reflection包中,它对常见的反射操作做了封装,提供了更加简洁方便的反射API。
2. Reflector&ReflectorFactory
2.1. Reflector
Reflector是Mybatis中反射模块的基础,每个Reflector对象都对应一个类,在Reflector中缓存了反射操作需要使用的类的元信息。Reflector中各个字段的含义如下所示:
/**
* 对应类的类型
*/
private final Class<?> type;
/**
* 可读属性的名称集合,可读属性就是存在相应的getter方法的属性,初始值为空数组
*/
private final String[] readablePropertyNames;
/**
* 可写属性的名称集合,可写属性就是存在相应setter方法的属性,初始值为空数组
*/
private final String[] writablePropertyNames;
/**
* 记录了属性相应的setter方法,key是属性名称,value是Invoke对象,它是对setter方法对应Method对象的封装,后面会详细介绍
*/
private final Map<String, Invoker> setMethods = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 记录了属性相应的getter方法集合,key是属性名称,value是Invoke对象,
*/
private final Map<String, Invoker> getMethods = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 记录了属性相应的setter方法的参数值类型,key是属性名称,value是setter方法的参数类型
*/
private final Map<String, Class<?>> setTypes = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 记录了属性相应的getter方法的返回值类型,key是属性名称,value是getter方法的返回值类型
*/
private final Map<String, Class<?>> getTypes = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 记录了默认的构造方法
*/
private Constructor<?> defaultConstructor;
/**
* 记录了所有属性名称的集合
*/
private Map<String, String> caseInsensitivePropertyMap = new HashMap<>(); 在Reflector的构造方法中会解析指定的Class对象,并填充上述集合,具体实现如下所示:
/**
* 此构造方法中会解析指定的Class对象,并填充上述集合
* @param clazz 需要解析的Class对象
*/
public Reflector(Class<?> clazz) {
//初始化type字段
type = clazz;
//查找clazz的默认构造方法(无参构造方法),具体实现是通过反射遍历所有构造方法
addDefaultConstructor(clazz);
//处理clazz中的getter方法,填充getMethods集合和getTypes集合
addGetMethods(clazz);
//处理clazz中的setter方法,填充setMethods集合和setTypes集合
addSetMethods(clazz);
//处理没有getter/setter方法的字段
addFields(clazz);
//根据getMethods和setMethods集合,初始化可读、可写属性的名称集合
readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
writablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
//初始化caseInsensitivePropertyMap,其中记录了所有大写格式的属性名称
for (String propName : readablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
for (String propName : writablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
}
以上代码中addDefaultConstructor(clazz);很是简单,所以没有必要去分析这个方法,其次就是addGetMethods(clazz);和addSetMethods(clazz);方法,Reflector.addGetMethods()方法主要腹泻解析类中定义的getter方法,Reflector.addSetMethods()方法负责解析类中的setter方法,两者的逻辑类似,这里以addSetMethods(clazz);方法为例进行介绍,addSetMethods()方法不做详细介绍,Reflector.addGetMethods()主要有如下三个核心步骤:
/**
* 负责解析类中的get方法
* @param clazz
*/
private void addGetMethods(Class<?> clazz) {
Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters = new HashMap<>();
/**
* 1. 调用{@link Reflector#getClassMethods(Class)} 方法获取当前类以及其父类中定义的所有方法的唯一签名以及相应的Method对象。
*/
Method[] methods = getClassMethods(clazz);
/**
* 2. 按照JavaBean的规范,从Reflector#getClassMethods(Class)方法返回的Methods数组中查找该类中定义的getter方法,
* 将其记录在conflictingGetters集合中,conflictingGetters集合( Map<String, List<Method>>类型)的key为属性名称,value是该属性对应的getter方法集合。
*
* 2.1. 具体步骤
* 2.1.1. 得到所有的get方法,(参数类别为空,标志是get的方法);
* 2.1.2. 将得到的get方法添加到方法冲突集合中;
* 例如:父类 public List<User> getUserList(); 子类 public ArrayList<User> getUserList();
* 在进行{@link Reflector#getClassMethods(Class)}中的{@link Reflector#getSignature(Method)}返回结果是:
* java.util.List#getUserList和java.util.ArrayList#getUserList,即得到两个方法签名,在{@link Reflector#addUniqueMethods(Map, Method[])}
* 方法中会被认为是两个不同的方法添加到 uniqueMethods集合中,这显然不是我们想要的结果。
*
* 所以后续步骤3 会去解决这种Getter方法的冲突。
*
* (lambda表达式 :filter forEach )
*/
Arrays.stream(methods).filter(m -> m.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && PropertyNamer.isGetter(m.getName()))
.forEach(m -> addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(m.getName()), m));
/**
* 3. 解决Getter冲突
* 1. 为什么会产生冲突呢?
* 步骤2已经解释过为什么会产生冲突了。
* 2. 解决方式是什么?
*/
resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters);
}首先,调用
Reflector.getClassMethods()方法获取当前类及其父类中定义的所以方法的唯一签名以及相应的Methods对象。private Method[] getClassMethods(Class<?> clazz) { Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods = new HashMap<>(); Class<?> currentClass = clazz; while (currentClass != null && currentClass != Object.class) { //记录currentClass这个类中定义的全部方法 addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, currentClass.getDeclaredMethods()); // we also need to look for interface methods - // because the class may be abstract // 记录接口中定义的方法 Class<?>[] interfaces = currentClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> anInterface : interfaces) { addUniqueMethods(uniqueMethods, anInterface.getMethods()); } //获取父类,继续while循环 currentClass = currentClass.getSuperclass(); } Collection<Method> methods = uniqueMethods.values(); //转换成Methods方法数组返回 return methods.toArray(new Method[0]); }在
Reflector.addUniqueMethods()方法中会为每个方法生成唯一签名,并记录到uniqueMethods集合中,具体实现如下所示:/** * 为每个方法生成一个唯一签名,并记录到uniqueMethods集合中 * @param uniqueMethods * @param methods */ private void addUniqueMethods(Map<String, Method> uniqueMethods, Method[] methods) { for (Method currentMethod : methods) { if (!currentMethod.isBridge()) { /** * 通过{@link Reflector#getSignature(Method)}方法得到方法的签名是:返回值类型#方法名称:参数类型列表。 * 例如: Reflector.getSignature(Method)的方法签名是:java.lang.String#getSignature:java.lang.reflect.Method * 通过Reflector.getSignature(Method)方法得到的方法签名是全局唯一的,可以作为该方法的唯一标识 */ String signature = getSignature(currentMethod); // check to see if the method is already known // if it is known, then an extended class must have // overridden a method /** * 检查是否添加过该方法,如果添加过,就无须在向uniqueMethods中添加该方法了。 * 其实这个段代码,如果细品有另一种意思: * 因为addUniqueMethods方法在{@link Reflector#getClassMethods(Class)}中的while循环被调用了,一次循环被调用两次, * 这两次调用:先是子类调用,然后是父类接口调用, * 所以这里检查是否添加过该方法的另一层含义是: * 检测是否在子类中已经添加过该方法,如果在子类中添加过,则表示子类覆盖了该方法,无须再向uniqueMethods集合中添加该方法了。 * */ if (!uniqueMethods.containsKey(signature)) { //记录该签名和方法的对应关系 uniqueMethods.put(signature, currentMethod); } } } }然后,按照
JavaBean的规范,从Reflector.getClassMethods()返回的Method数组中查找该类中定义的getter方法(具体哪些方法算是getter方法,后面会详细介绍),将其记录到conflictingGetters集合中。conflictingGetters集合(Map<String, List<Method>>类型)的key是属性名称,value是该属性对应的getter方法集合。//Reflector.java Arrays.stream(methods).filter(m -> m.getParameterTypes().length == 0 && PropertyNamer.isGetter(m.getName())) .forEach(m -> addMethodConflict(conflictingGetters, PropertyNamer.methodToProperty(m.getName()), m));//Reflector.java /** * 添加方法冲突 * @param conflictingMethods * @param name * @param method * */ private void addMethodConflict(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingMethods, String name, Method method) { if (isValidPropertyName(name)) { /** * {@link Map#computeIfAbsent(Object, Function)} * @see red.reksai.reflection.ComputeIfAbsentTest map jdk1.8新特性 */ List<Method> list = conflictingMethods.computeIfAbsent(name, k -> new ArrayList<>()); list.add(method); } }//PropertyNamer.java /** * 根据Javabean的规范,获取对应的属性名称 * @param name * @return */ public static String methodToProperty(String name) { if (name.startsWith("is")) { name = name.substring(2); } else if (name.startsWith("get") || name.startsWith("set")) { name = name.substring(3); } else { throw new ReflectionException("Error parsing property name '" + name + "'. Didn't start with 'is', 'get' or 'set'."); } if (name.length() == 1 || (name.length() > 1 && !Character.isUpperCase(name.charAt(1)))) { name = name.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH) + name.substring(1); } return name; }当子类覆盖了父类的getter方法且返回值发生变化时,在步骤1中就会产生两个签名不用的方法。
- 例如:
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.Reflector; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author : <a href="mailto:gnehcgnaw@gmail.com">gnehcgnaw</a> * @since : 2019/11/26 10:19 */ public class ReflectorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Reflector reflector = new Reflector(User.class); System.out.println(reflector); } } class User extends Person{ public User() { } public User(String userName, String passWord) { this.userName = userName; this.passWord = passWord; } private String userName ; private String passWord ; public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getPassWord() { return passWord; } public void setPassWord(String passWord) { this.passWord = passWord; } public boolean isStatus() { return super.getStatus() ; } @Override public void setStatus(boolean status) { super.setStatus(status); } @Override public ArrayList<Items> getList() { return (ArrayList<Items>) super.getList(); } @Override public void setList(List<Items> list) { super.setList(list); } } class Person { private List<Items> list; private boolean status ; public boolean getStatus() { return status; } public void setStatus(boolean status) { this.status = status; } public List<Items> getList() { return list; } public void setList(List<Items> list) { this.list = list; } public Person() { } public Person(List<Items> list) { this.list = list; } } class Items{ private String itmeId; private String itmeName ; }- 在以下位置打断点
- 观察conflictingGetters集合中的值,如下所示:
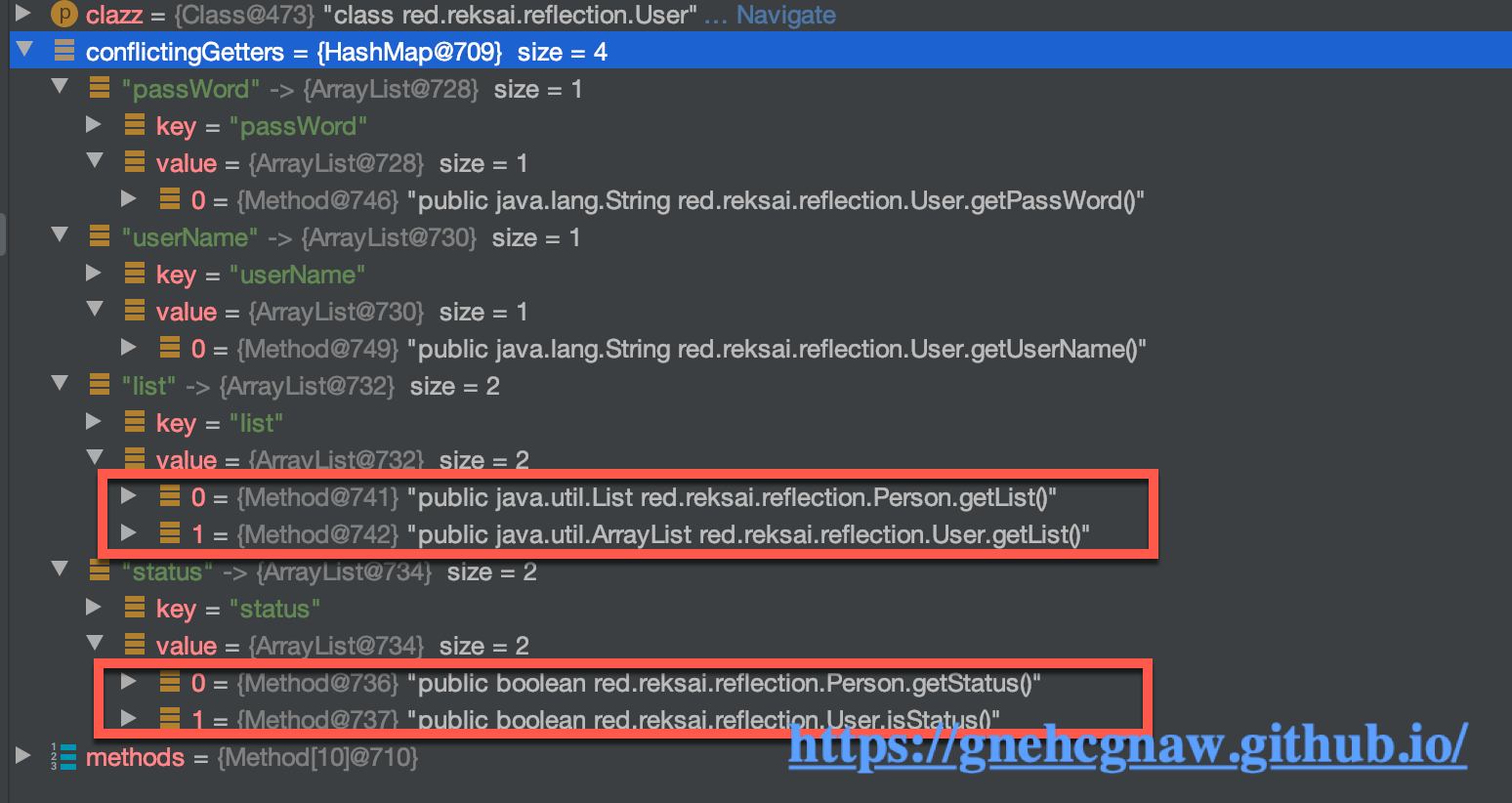
其中属性名称为
list对应的getter方法的集合中有两个Method,这就是因为User在覆盖Person中的getList()方法是返回值从List变成了ArrayList,又因为生成方法签名的规则如下所示,所以就造成了有两个不同方法签名的方法被添加到了uniqueMethods集合中,这不是我们想要的结果。// Reflector.java /** * 生成方法签名 * @param method * @return */ private String getSignature(Method method) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (returnType != null) { sb.append(returnType.getName()).append('#'); } sb.append(method.getName()); Class<?>[] parameters = method.getParameterTypes(); for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) { sb.append(i == 0 ? ':' : ',').append(parameters[i].getName()); } return sb.toString(); }其中属性为
status对应的getter方法的集合中有两个Method,一个是父类中的boolean getStatus(),另一个是子类中的boolean isStatus()(涉及到JavaBean规范),说白了此时uniqueMethods集合中也有两个,这也不是我们想要的结果。所以步骤3会调用
Reflector.resolveGetterConflicts(conflictingGetters)方法对步骤2中这种覆写的情况进行处理,同时会将处理得到的getter方法记录到getMethods集合中,并将其返回值类型填充到getTypes集合中,Reflector.resolveGetterConflicts()方法的具体实现如下所示:
//Reflector.java
/**
* 解决get方法的冲突,同时会将处理得到的getter方法记录到getMethods集合中,并将其返回值类型填充到getTypes集合中
* @param conflictingGetters
*/
private void resolveGetterConflicts(Map<String, List<Method>> conflictingGetters) {
//遍历conflictingGetters集合
for (Entry<String, List<Method>> entry : conflictingGetters.entrySet()) {
//优胜Method对象
Method winner = null;
//方法名称
String propName = entry.getKey();
boolean isAmbiguous = false;
// candidate 候选Method对象
for (Method candidate : entry.getValue()) {
//如果优胜对象为空,这时候将候选对象复制给优胜对象
if (winner == null) {
winner = candidate;
// continue是跳过当次循环中剩下的语句,执行下一次循环
continue;
}
//获取优胜者返回值类型
Class<?> winnerType = winner.getReturnType();
//获取候选者返回值类型
Class<?> candidateType = candidate.getReturnType();
/**
* 如果返回值类型相同,就要判断返回值是不是boolean?为什么要判断是不是boolean呢?
*/
if (candidateType.equals(winnerType)) {
//如果返回值不是boolean直接
if (!boolean.class.equals(candidateType)) {
isAmbiguous = true;
//break只能跳出1层循环
break;
} else if (candidate.getName().startsWith("is")) {
winner = candidate;
}
}
/**
* @see red.reksai.javabase.IsAssignableFromTest
* 判断返回值类型有三种情况:
* 1. 候选者是优胜者的父类,不做任何操作,最终返回子类就行
* 2. 优胜者是候选者的父类,这时候先要将候选者赋值给优胜者,然后返回
* 3. 返回值相同,二义性,
*/
else if (candidateType.isAssignableFrom(winnerType)) {
// OK getter type is descendant
} else if (winnerType.isAssignableFrom(candidateType)) {
winner = candidate;
} else {
isAmbiguous = true;
break;
}
}
//该字段只有一个getter方法,直接添加到getMethods集合并填充getTypes集合
addGetMethod(propName, winner, isAmbiguous);
}
}正如上面描述的那样,在Reflector.addGetMethod(propName, winner, isAmbiguous);方法中完成了对getMethods集合和getType集合的填充,具体实现如下所示:
private void addGetMethod(String name, Method method, boolean isAmbiguous) {
/**
* 验证:
* 1. 如果有含糊不清的直接报错,
* 2. 如果验证通过,则进行方法的封装
*/
MethodInvoker invoker = isAmbiguous
? new AmbiguousMethodInvoker(method, MessageFormat.format(
"Illegal overloaded getter method with ambiguous type for property ''{0}'' in class ''{1}''. This breaks the JavaBeans specification and can cause unpredictable results.",
name, method.getDeclaringClass().getName()))
: new MethodInvoker(method);
getMethods.put(name, invoker);
/**
* 获取返回值的Type ,{@link TypeParameterResolver}
*/
Type returnType = TypeParameterResolver.resolveReturnType(method, type);
getTypes.put(name, typeToClass(returnType));
}2.2. TypeParameterResolver
2.3. ObjectFactory
Mybatis中有很多模块会使用到ObjectFactory接口,该接口提供了多个create()方法的重载,通过这些方法可以创建指定类型的对象,ObjectFactory接口的定义如下所示:
/**
* Mybatis中有很多模块会使用到ObjectFactory接口,该接口提供了多个create()方法的重载,
* 通过这些方create()方法可以创建指定类型的对象。
* @see DefaultObjectFactory
* MyBatis uses an ObjectFactory to create all needed new Objects.
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface ObjectFactory {
/**
* 设置配置信息
* Sets configuration properties.
* @param properties configuration properties
*/
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
/**
* 空操纵:说白了,如果要继承ObjectFactory,不仅要定义Properties 属性,还有再提供一个getProperties()的方法
* e.g. {@link red.reksai.mybatissample.objectfactory.ExampleObjectFactory}(我自定义的测试用例)
* {@link org.apache.ibatis.submitted.global_variables_defaults.SupportClasses.CustomObjectFactory}(官方测试用例)
* 同时在mybatis-config.xml添加如下配置:
* <objectFactory type="org.mybatis.example.ExampleObjectFactory">
* <property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
* </objectFactory>
* 这样可以拿到property的值。
*/
// NOP
}
/**
* 通过无参构造器创建指定类的对象
* Creates a new object with default constructor.
* @param type Object type
* @return
*/
<T> T create(Class<T> type);
/**
* 根据参数列表,从指定的类型中选择合适的构造器创建对象
* Creates a new object with the specified constructor and params.
* @param type Object type
* @param constructorArgTypes Constructor argument types
* @param constructorArgs Constructor argument values
* @return
*/
<T> T create(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs);
/**
* 检测指定类型是否是集合类型,主要处理java.util.Collection及其子类
* Returns true if this object can have a set of other objects.
* It's main purpose is to support non-java.util.Collection objects like Scala collections.
*
* @param type Object type
* @return whether it is a collection or not
* @since 3.1.0
*/
<T> boolean isCollection(Class<T> type);
}
DefaultObjectFactory是Mybatis提供的ObjectFactory接口的唯一实现,它是一个反射工厂,其create()方法通过调用instanceClass()方法实现。DefaultObjectFactory.instanceClass()方法会根据传入的参数列表选择合适的构造函数实例化对象,具体实现如下:
private <T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs) {
try {
Constructor<T> constructor;
//通过无参构造器创建对象
if (constructorArgTypes == null || constructorArgs == null) {
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor();
try {
return constructor.newInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor.newInstance();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
//根据指定的参数列表查找构造函数,并实例化对象
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor(constructorArgTypes.toArray(new Class[constructorArgTypes.size()]));
try {
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[constructorArgs.size()]));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
if (Reflector.canControlMemberAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[constructorArgs.size()]));
} else {
throw e;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String argTypes = Optional.ofNullable(constructorArgTypes).orElseGet(Collections::emptyList)
.stream().map(Class::getSimpleName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
String argValues = Optional.ofNullable(constructorArgs).orElseGet(Collections::emptyList)
.stream().map(String::valueOf).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
throw new ReflectionException("Error instantiating " + type + " with invalid types (" + argTypes + ") or values (" + argValues + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
除了使用Mybatis提供的DefaultObjectFactory实现,我们还可以在mybatis-config.xml配置文件中指定自定义的ObjectFactory接口实现类,从而实现功能上的扩展,在后面介绍Mybatis初始化流程的时候,还会提到该扩展点。
2.4. Property工具集
本小节主要介绍反射模块中使用到的三个属性工具类,分别是PropertyTokenizer、PropertyNamer和PropertyCopier。
此段我暂时也不知道怎么去解释,也许是后续学习能解释这个问题吧。
在使用Mybatis的过程中,我们会经常碰到一些属性表达式,例如,在查询某用户(User)的订单(Order)的结果集如下表所示:
| user_name | order | item1 | item2 | . . . |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mary | 12460 | IPhone | Computer | |
| Lisa | 36546 | MX | Wather | |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . |
2.4.1. PropertyTokenizer
PropertyTokenizer是一个属性分词器工具,它继承了Iterator接口,它可以迭代处理嵌套的多层表达式。
由“*”和“[]”组成的表达式是由PropertyTokenizer进行解析的,PropertyTokenizer中各个字段的含义如下所示:
// fullName = "order[0].items[0].name"
// String[] split = {"order[0]" ,"item[0]" ,"name"}
/**
* 当前表达式的名称:
* e.g. order
* items
* name
*/
private String name;
/**
* 当前表达式的索引名
* e.g. order[0]
* items[0]
* name
*/
private final String indexedName;
/**
* 索引下标
* e.g. [0]
* [0]
* null
*/
private String index;
/**
* 子表达式
* e.g. items[0].name
* name
* null
*/
private final String children;
核心方法有三个分别是:
PropertyTokenizer()
/**
* 解析表达式
* @param fullname 要解析的表达式
* e.g. order[0].items[0].name
*/
public PropertyTokenizer(String fullname) {
//查找"."的位置
int delim = fullname.indexOf('.');
if (delim > -1) {
//初始化name
name = fullname.substring(0, delim);
//初始化children
children = fullname.substring(delim + 1);
} else {
name = fullname;
children = null;
}
//初始化indexName
indexedName = name;
//查找"["的位置,如果存在,最后要把上面步骤赋值给name中的"[]"去掉
delim = name.indexOf('[');
if (delim > -1) {
//初始化index
index = name.substring(delim + 1, name.length() - 1);
//重新赋值给name
name = name.substring(0, delim);
}
}hasNext()
/**
* 判断是否还有children
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return children != null;
}
next()
/**
* 继续解析孩子节点
* @return
*/
@Override
public PropertyTokenizer next() {
return new PropertyTokenizer(children);
}例子:
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.property.PropertyTokenizer;
/**
* @author : <a href="mailto:gnehcgnaw@gmail.com">gnehcgnaw</a>
* @since : 2019/11/29 11:12
*/
public class PropertyTokenizerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String fullName = "orders[0.items[0].name" ;
doTokenizer(fullName);
}
private static void doTokenizer(String name){
PropertyTokenizer propertyTokenizer = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
System.out.println(propertyTokenizer.getIndexedName());
System.out.println(propertyTokenizer.getName());
System.out.println(propertyTokenizer.getIndex());
System.out.println(propertyTokenizer.getChildren());
System.out.println(".................");
String children = propertyTokenizer.getChildren();
if (propertyTokenizer.hasNext()){
doTokenizer(children);
}
}
}运行结果:
orders[0
orders
items[0].name
.................
items[0]
items
0
name
.................
name
name
null
null
.................2.4.2. PropertyNamer
2.4.3. PropertyCopier
2.5. MetaClass
2.5.1. 主要方法详解
MetaClass通过Reflector和PropertyTokenizer组合使用,实现了对复杂的属性表达式的解析,并实现了获取指定属性描述信息的功能。MetaClass中各个字段的含义如下:
/**
* ReflectorFactory对象,用于缓存Reflector对象
*/
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
/**
* 在创建MetaClass时会指定一个类,该Reflector对象会用于记录该类相关信息
*/
private final Reflector reflector;MetaClass的构造函数中会为指定的Class创建相应的Reflector对象,并用其初始化MetaClass.reflector字段,具体代码如下所示:
/**
* 此构造方法是一个private
* @param type
* @param reflectorFactory
*/
private MetaClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
this.reflectorFactory = reflectorFactory;
//创建reflector对象,默认使用的是DefaultReflectorFactory.findForClass()方法
this.reflector = reflectorFactory.findForClass(type);
}
/**
* 使用静态方法创建MetaClass对象
* @param type
* @param reflectorFactory
* @return
*/
public static MetaClass forClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
return new MetaClass(type, reflectorFactory);
}MetaClass中比较重要的是findProperty()方法,它是通过调用MetaClass.buildProperty()方法实现的:
//MetaClass.java
/**
* 只查找"."导航的属性,并且没有检测下标
* @param name 要查找的属性名称
* @return
*/
public String findProperty(String name) {
//委托给buildProperty()方法实现
StringBuilder prop = buildProperty(name, new StringBuilder());
return prop.length() > 0 ? prop.toString() : null;
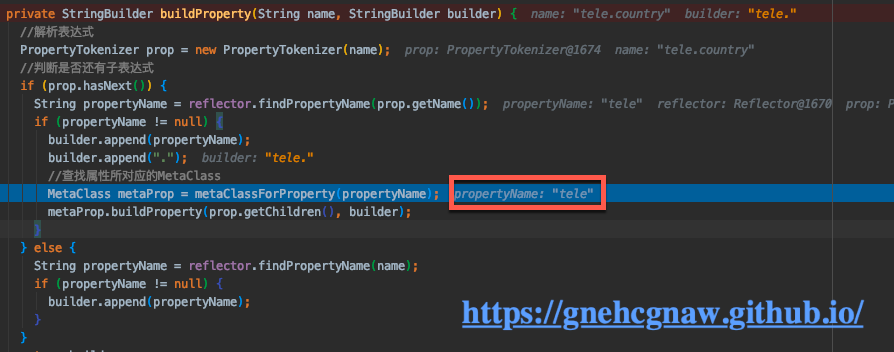
} private StringBuilder buildProperty(String name, StringBuilder builder) {
//解析表达式
PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
//判断是否还有子表达式
if (prop.hasNext()) {
String propertyName = reflector.findPropertyName(prop.getName());
if (propertyName != null) {
builder.append(propertyName);
builder.append(".");
//查找属性所对应的MetaClass
MetaClass metaProp = metaClassForProperty(propertyName);
metaProp.buildProperty(prop.getChildren(), builder);
}
} else {
String propertyName = reflector.findPropertyName(name);
if (propertyName != null) {
builder.append(propertyName);
}
}
return builder;
}有上述代码可以看出:findPropertory()方法值查找“.”导航的属性,并没有检测下标。
这里以解析User类中的tele.contry这个属性表达式为例解释上述过程:
首先使用findPropertory(“tele.contry”);
MetaClass.buildPropertry(“tele.country”,stringBuilder);
接着使用PropertryTokenizer解析数据,发现还有子表达式:country,说明此属性表达式所属的类不是当前了,需要查找此属性属于的类;
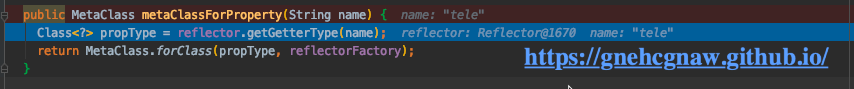
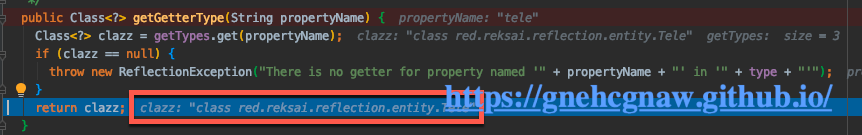
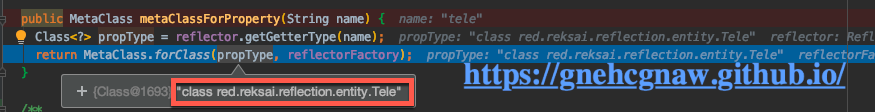
所以要通过MetaClass.metaClassForPropertry(“tele”),获取到对应的实体类,其中使用到了Reflector.getGetterType()得到了返回值的类型,然后使用MetaClass.forClass()返回返回值对应的元类。
递归调用2。

2.5.2. 测试用例
package red.reksai.reflection;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.DefaultReflectorFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaClass;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import red.reksai.reflection.entity.User;
/**
* @author : <a href="mailto:gnehcgnaw@gmail.com">gnehcgnaw</a>
* @since : 2019/11/29 10:07
*/
public class MetaClassTest {
@Test
public void test() {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(User.class, new DefaultReflectorFactory());
System.out.println(metaClass.findProperty("tele.country")); //tele.country
System.out.println(metaClass.getGetterType("tele.country")); // class java.lang.String
System.out.println(metaClass.hasGetter("tete.country")); //true
System.out.println(metaClass.getGetterType("orders[0].items[0]")); // class red.reksai.reflection.entity.Item
}
}
2.6. ObjectWrapper
2.7. MetaObject
2.8. ParamNameResolver
ParamNameResolver是参数名称解析器,把传入的实参,解析成对象,分为两种:一种是不加@Param注解的;一种是加了注解的,Mybatis源码中的使用场景在后续介绍,使用的类有:
- MapperMethod
- ProviderSqlSource
- Jdbc3KeyGenerator
/**
* 参数名称解析器
*/
public class ParamNameResolver {
/**
* 通用前缀,假如没有定义参数名称,最后在同一个方法的参数列表就是param1 、param2 一次类推。
*/
public static final String GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX = "param";
/**
* 参数的名称是有顺序的
* <p>
* The key is the index and the value is the name of the parameter.<br />
* The name is obtained from {@link Param} if specified. When {@link Param} is not specified,
* the parameter index is used. Note that this index could be different from the actual index
* when the method has special parameters (i.e. {@link RowBounds} or {@link ResultHandler}).
* </p>
* <ul>
* <li>aMethod(@Param("M") int a, @Param("N") int b) -> {{0, "M"}, {1, "N"}}</li>
* <li>aMethod(int a, int b) -> {{0, "0"}, {1, "1"}}</li>
* <li>aMethod(int a, RowBounds rb, int b) -> {{0, "0"}, {2, "1"}}</li>
* </ul>
*/
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> names;
/**
* 参数是否被注解注释
*/
private boolean hasParamAnnotation;
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {
final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;
// get names from @Param annotations
for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {
if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {
// skip special parameters
continue;
}
String name = null;
for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {
if (annotation instanceof Param) {
hasParamAnnotation = true;
name = ((Param) annotation).value();
break;
}
}
if (name == null) {
// @Param was not specified.
if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {
name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);
}
if (name == null) {
// use the parameter index as the name ("0", "1", ...)
// gcode issue #71
name = String.valueOf(map.size());
}
}
map.put(paramIndex, name);
}
names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
private String getActualParamName(Method method, int paramIndex) {
return ParamNameUtil.getParamNames(method).get(paramIndex);
}
private static boolean isSpecialParameter(Class<?> clazz) {
return RowBounds.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) || ResultHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
}
/**
* Returns parameter names referenced by SQL providers.
*/
public String[] getNames() {
return names.values().toArray(new String[0]);
}
/**
* <p>
* A single non-special parameter is returned without a name.
* Multiple parameters are named using the naming rule.
* In addition to the default names, this method also adds the generic names (param1, param2,
* ...).
* </p>
*/
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = names.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
}
// 没有加注解,并且只有一个参数的时候就返回第一个就就行,这样是为了节省性能
else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {
return args[names.firstKey()];
}
/**
* 假如加了注解,返回的参数形式就有两套:
* e.g.
* @Param 这是一套
* param1, param2, ...这是另一套
*/
else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// add generic param names (param1, param2, ...)
final String genericParamName = GENERIC_NAME_PREFIX + String.valueOf(i + 1);
// ensure not to overwrite parameter named with @Param
if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
}
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!